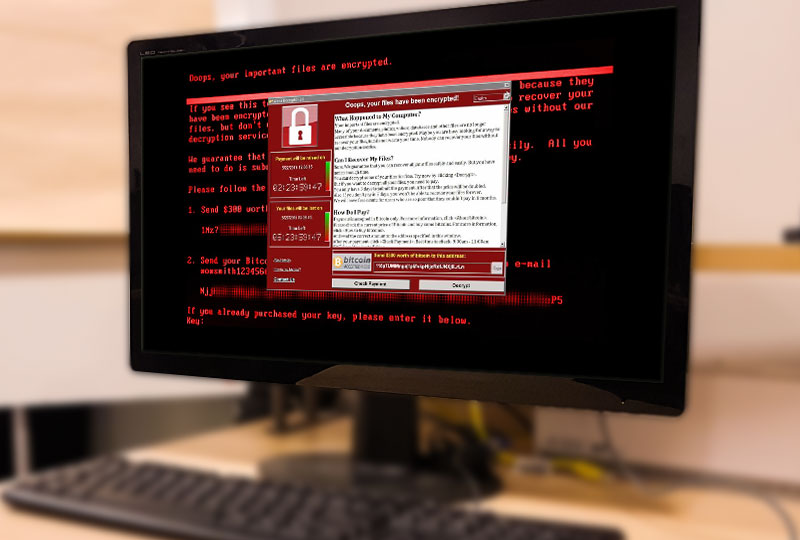
Malicious Ransom Software, popularly known as ransomware, is a type of malware (malicious software) designed to prevent access to a system or files on a system until the attackers get paid. Commonly done by encrypting your files, and asking for payment to receive the key to unlock them.
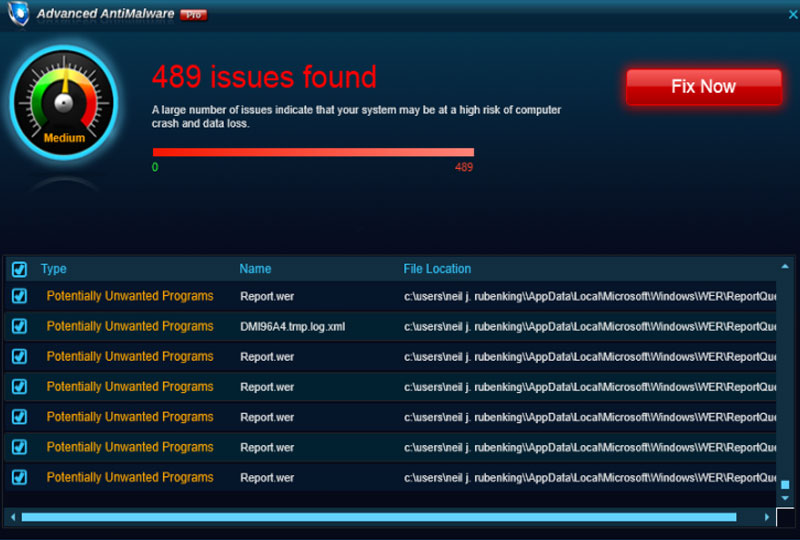
There are three types of ransomware. Firstly, you have scareware. These are the pop ups that tell you that your computer is infected and that you need to buy this security software to clear your computer, or that a website has detected fraudulent behaviour and you need to call this helpline for support. Apart from these pop-ups, usually from a malicious redirect, there is nothing wrong with your computer.
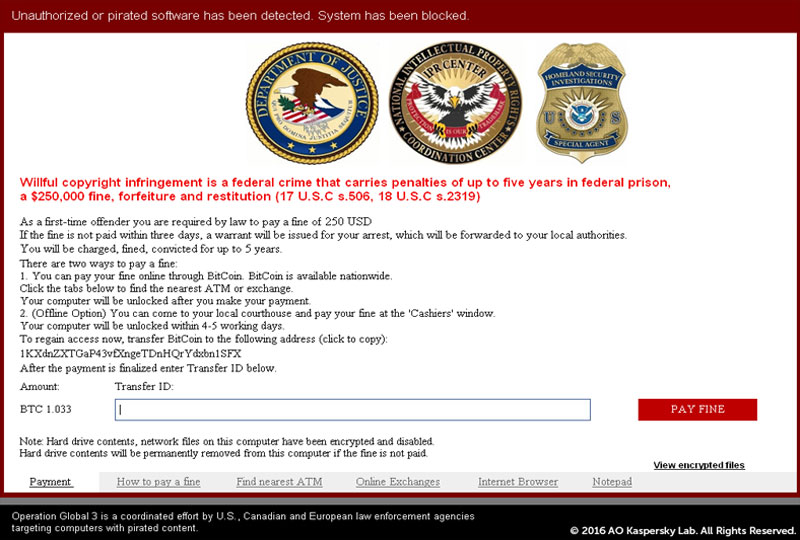
Next you have screen lockers. These hijack your desktop and provide a full-size window, usually stating that a security service has found illegal activity on your computer, and a fine must be paid. This type of ransomware will make your operating system unusable, but usually your files will be left untouched and can be recovered.
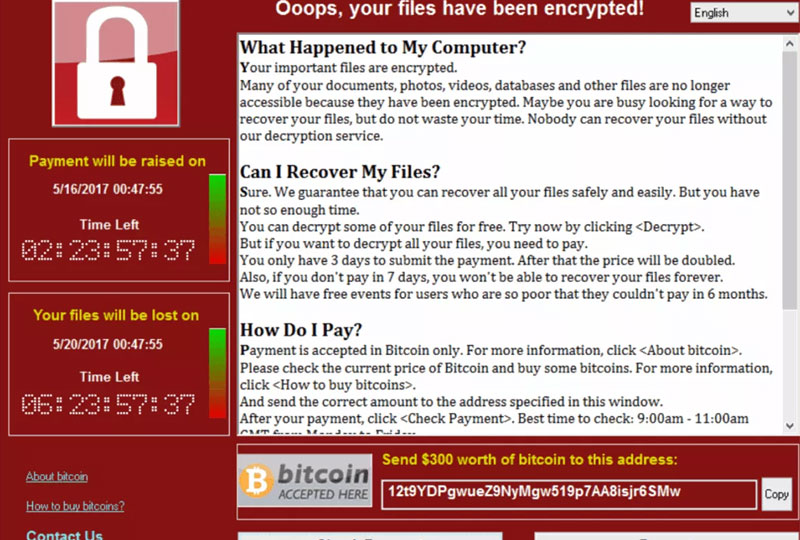
And finally, you have File encryption ransomware. This type of ransomware is the scariest, as once you have been infected by it, there’s usually a very slim chance of you getting your data back. This ransomware encrypts your files, making them unreadable without a special key that is kept away from you until the ransom is paid.
Ransomware is mostly spread through Trojan Horses that disguise themselves as something useful that you would want to install. Alongside this new application, the ransomware works in the background, and encrypts your files. A note is then left with these encrypted files, giving directions on how to recover your files. Ransomware can also spread through malicious spam, with emails containing an infected word document or links to malicious websites.
To avoid becoming infected with ransomware, there are three important steps to take:
- Make sure to only download files from secure and trusted sources, run any downloaded file through anti-virus software, and have an anti-virus software with real time protection.
- Make sure that all your programs and operating systems are up to date, as a lot of these exploits rely on vulnerabilities in programs.
- Last, but most importantly, make sure that you have a backup of all important files and data in case an infection does happen. This way all the data that they’re attacking will be safe and easily recovered.
It is recommended to not pay the ransom, as even if it is paid, there is a chance you won’t receive the decryption key. Paying also tells the attackers that this works, and will make further attacks more likely. Because Ransomware uses encryption, recovering from an attack can be extremely difficult, and cannot be guaranteed, but many security firms have been working on decryption tools that can be used to try and reverse the encryption.